SSH is a tool used to connect to your server. This is how the majority of your system is setup.
To use ssh, you'll need an ssh client for your local computer. We recommend PuTTY.
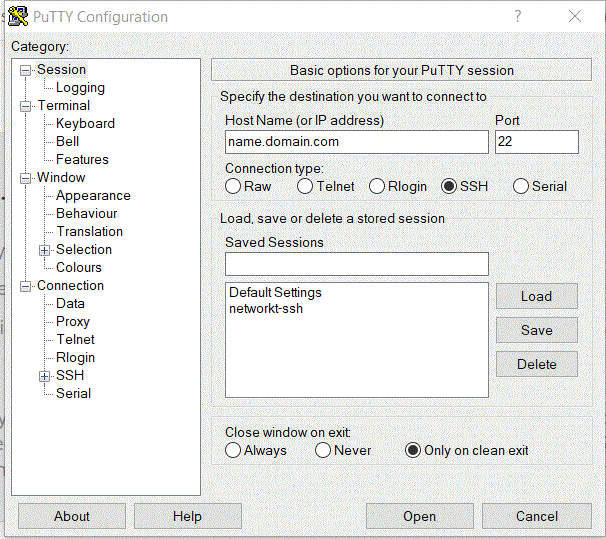
Once you've installed your ssh client, load it up and you should be given a space to enter some information. You'll want to select "SSH" on port 22. You can paste in the Hostname of your server "name.domain.com" or the ip "1.2.3.4" in the the space that says "Host Name (or IP Address)". Click "Open".
If you've entered all info correctly, you should be prompted with a large black screen asking for your login information. If you are doing system tasks, you'll probably need root access. If you have root access, enter "root" and press enter. Sometimes, it can take several seconds before you see any change. Enter the root password (and press enter), and if everything works, you should see a command prompt, ex:
[root@server]#
You are now logged into the server. This is your starting point.
From here you can do anything, including destroy your server, so you must be very careful with the commands you enter.
Some basic commands include:
List: ls
[root@server]# ls file1.txt file2.txt file3.txt
Change Directories: cd
[root@server]# cd /home/admin
Remove a file: rm
[root@server]# rm file1.txt
rm: remove `file1.txt' ? y
Once you've finished working, you can type "exit" and the ssh window should close.
[root@server]# exit
For a more comprehensive list, visit Command Line Tools for Managing Linux Server.
 👀 Choose SSD-powered VPS servers for increased speed, power, and security! Now 50% off- starting from only $1.99/mo.
👀 Choose SSD-powered VPS servers for increased speed, power, and security! Now 50% off- starting from only $1.99/mo.


